Key takeaways:
- Immersive virtual reality and augmented reality will spearhead the new wave of 5G-boosted experiences underpinned by mobile cloud.
- 5G provides a powerful tool for creating new blue ocean markets for business and will provide industry customers with the opportunity to revolutionize their business models.
Mobile broadband, cloud computing, and smart terminals enable ubiquitous connectivity, transforming the way we sense the world around us. By 2025, it’s estimated that the number of connected devices will hit 100 billion worldwide. From next-gen 5G communication networks, we can expect hundreds of billions of connections, ultra-low latency of 1 ms, and 10 Gbps transmission speeds.
Spanning all verticals, digital transformation is starting to shift user experience away from text, image, voice, and HD video. Immersive virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are destined to spearhead the new wave of 5G-boosted experiences underpinned by mobile cloud.
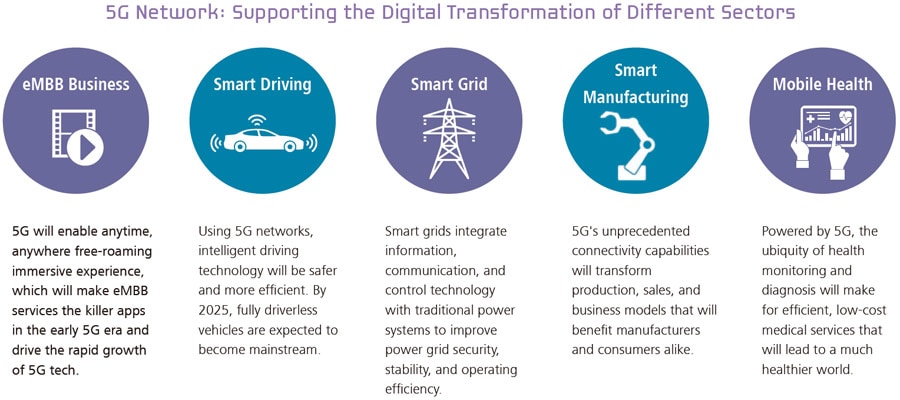
5G will focus communication networks away from people and onto things. It will integrate mobile tech, big data, IoT, and cloud computing, and give rise to applications like enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) services, intelligent driving, smart power grids, smart manufacturing, and mobile medicine.
eMBB: Always connected
MBB and smart devices will ensure that eMBB services and applications grow rapidly. Mobile video services already account for over 50 percent of the services delivered by telcos, and free-roaming VR and AR on mobile devices are emerging as the new direction for eMBB services. They will soon dominate social media, replacing text and image as the main information exchange mediums. To achieve this in high-traffic areas, Gpbs bandwidth and millisecond latency is essential for precise image processing, tracking, and transmission in real time.
5G will introduce new innovative solutions for uplink and downlink bandwidth, latency, network capacity, and energy-saving for a fantastic mobile experience.
The transition from 4K/8K HD video to anytime, anywhere free-roaming immersive services on mobile devices will place massive bandwidth demands on the connectivity capabilities of network pipes. The strong demand for these services will make them the killer apps in the early 5G era and drive the rapid growth of 5G tech.
Smart driving hits the streets
Intelligent connected driving will connect vehicles to other vehicles and also to pedestrians, roads, and networks. Alongside big data analytics, the vehicular infrastructure will be interconnected and aware, improving safety and flow and lowering emissions.
Current short-range wireless networks can support communication over small areas in ideal transmission conditions. However, non-line-of-sight (NLOS) communication involving complex road conditions or poor transmission environments complicates matters. Overviews of traffic information over wide areas for rapid alerts and collision avoidance are difficult with current technology. This is especially true in high-speed scenarios, where frequency offset, inter-cell handover, and interference from obstacles are all major issues because short-range networking tech is limited.
Cellular networks' propagation paths serving as connection channels will become far more significant as a result.
Using 5G networks, intelligent driving technology will be safer and more efficient. By 2025, fully driverless vehicles are expected to become mainstream.
More energy with smart grids
Smart grids integrate information, communication, and control technology with traditional power systems to improve power grid security, stability, and operating efficiency.
Many nations across the world are implementing smart grid projects. In America, for example, smart grid initiatives more or less cover the nation. In 2009 with an anticipated 1:1 government: private investment ratio, the American Recovery & Reinvestment Act (ARRA) allocated US$11 billion for smart grid investment covering 49 of 50 states. Numerous smart grid projects and R&D initiatives are also spread out over Europe.
Power generation facilities are undergoing the challenging process of digitizing form, scale, and power management and control. The communications systems for smart grids will cover all nodes on the power system, including power generation, transformation, transmission, distribution, and usage. Nodes in the power grid with communication requirements will include power generation facilities, transmission and distribution lines, substations, power plants, electricity meters, and dispatch centers. For example, with US$200 million in ARRA funding and US$378 million in private funding, the Florida Power & Light Company Smart Grid Project involves 2.6 million smart meters, 9,000 intelligent distribution devices, 45 phasors, and advanced monitoring equipment in over 270 substations.
End consumers of electricity are also becoming suppliers, providing power when they’re not using it in a bidirectional usage model.
New energy strategies aim to improve the power efficiency of power systems by building an Internet of Power supported by high capacity, high-speed, real-time, secure, and stable communications networks.
As an exceptional integrator, 5G can support the diverse requirements of smart grids. 5G supports flexible wireless over-the-air connectivity, has excellent disaster recovery capabilities, and is more efficient and faster than fiber optic and short range wireless communications technology.
This is particularly true when constructing networks in places with complex topography such as mountainous areas or areas with water features. 5G network technology also supports ultra-high bandwidth, NLOS transmission, wide-area seamless coverage, and roaming.
Smart manufacturing
Smart tech for manufacturing will be based on communications infrastructure with higher capacity, bandwidth, storage, and data processing capabilities. Equipment will be automated and the system will provide flexible human-computer interaction and smart control.
Emerging manufacturing services will extend the boundary of products to include value-added after-sale services based on interconnected and controllable data collection and transmission systems covering the entire product lifecycle.
Typical smart manufacturing application scenarios include real-time E2E production process control, remote control, internal and external enterprise communications, and IoT for cargo. It includes supply chain management models that unify full product lifecycle management on a single network. 5G networks’ wireless connectivity, high-speed, and low-latency capabilities will allocate supply chain resources and thus raise production and service efficiency.
5G's unprecedented connectivity capabilities will transform production, sales, and business models that will benefit manufacturers and consumers alike.
Mobile health for all
Mobile health applies mobile Internet tech to provide E2E healthcare, including disease prevention, counseling, treatment, and rehabilitation. Advanced wireless communications and information processing technology can streamline medical diagnosis and better allocate and share medical resources and data.
5G's advanced connectivity, integrated mobility, and big data analytics platform will give tomorrow's doctors the tools to achieve patient monitoring in real time and remote diagnosis. Patients will have access to remote monitoring and diagnostics through 5G networks and wearable devices that can quickly transmit their health status and symptoms and enable diagnoses.
 Institutions will be able to securely share electronic medical records between institutions. Medical practitioners will be able to monitor individual health trends and outcomes for tailored treatments, and correlate health status with factors like pollution, temperature, lifestyle, diet, and sleep based on ubiquitous sensors.
Institutions will be able to securely share electronic medical records between institutions. Medical practitioners will be able to monitor individual health trends and outcomes for tailored treatments, and correlate health status with factors like pollution, temperature, lifestyle, diet, and sleep based on ubiquitous sensors.
Powered by 5G, the ubiquity of health monitoring and diagnosis will make for efficient, low-cost medical services that will lead to a much healthier world.
Expanding business boundaries
Digital transformation is broadening and mixing business boundaries in all sectors, which will increase both diversity and uncertainty. But, with 5G’s network design concepts and integrative capabilities, it’s possible to combat these uncertainties. 5G provides a powerful tool for creating new blue ocean markets for businesses, and will provide industry customers the opportunity to revolutionize their businesses.
Connectivity drives socioeconomic digital transformation, with each generation of mobile technology offering different effects. With its unprecedented connectivity capabilities, 5G will take society to a whole new level, revolutionize industry and consumer experience, and truly make a Better Connected World possible.




 Institutions will be able to securely share electronic medical records between institutions. Medical practitioners will be able to monitor individual health trends and outcomes for tailored treatments, and correlate health status with factors like pollution, temperature, lifestyle, diet, and sleep based on ubiquitous sensors.
Institutions will be able to securely share electronic medical records between institutions. Medical practitioners will be able to monitor individual health trends and outcomes for tailored treatments, and correlate health status with factors like pollution, temperature, lifestyle, diet, and sleep based on ubiquitous sensors.