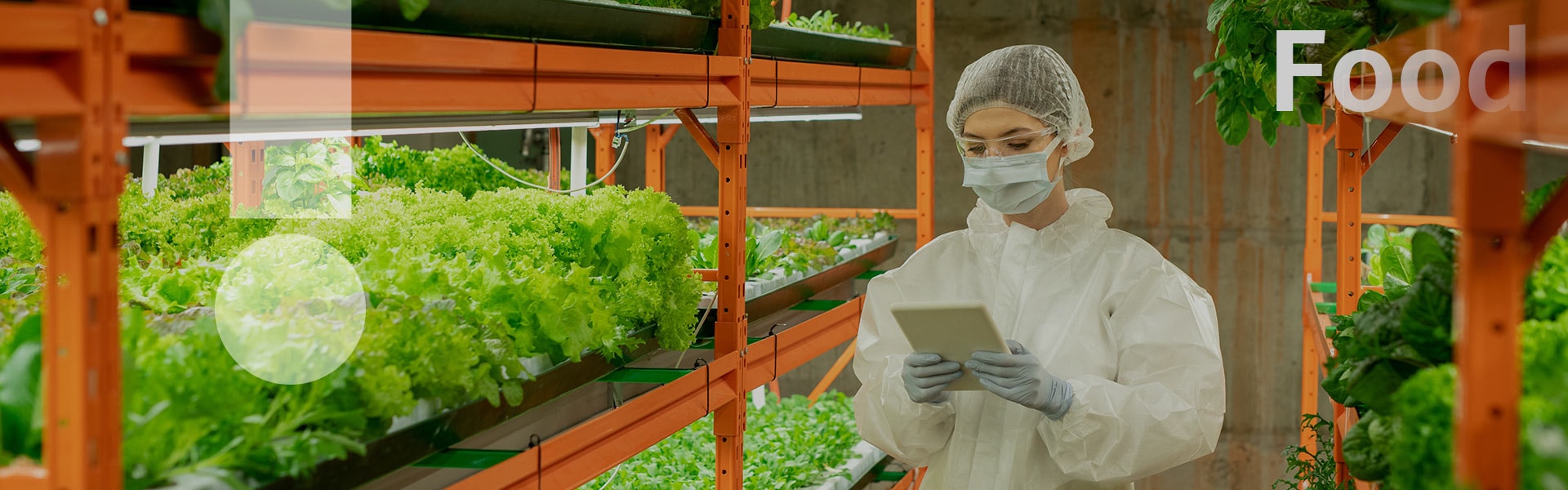
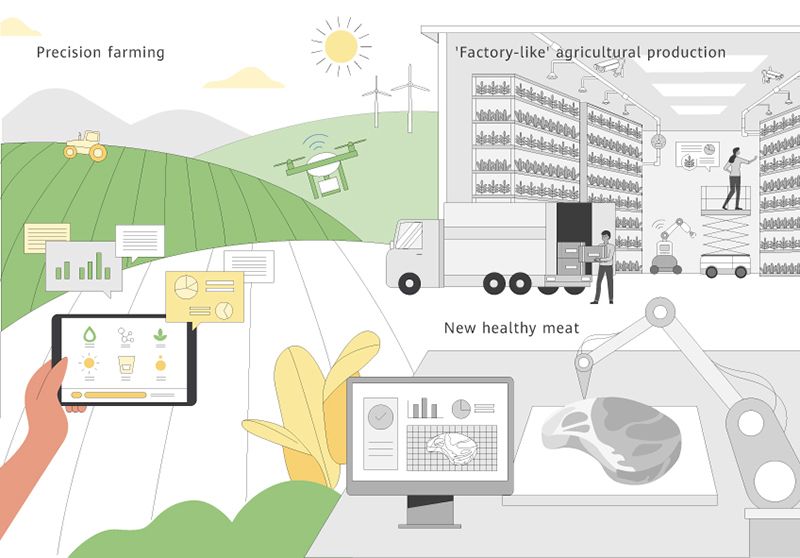
Data-driven Food Production for More Bountiful, Inclusive, and "Green" Diets
By 2030, visualized data graphs for agricultural production will make precision farming possible. Based on collected data, people will be able to control factors that affect crop growth, such as temperature and humidity, and create vertical farms unaffected by the uncertainties of climate and weather.
Predictions
Directions for Exploration
Using accurate data, not experience, to guide cultivation
Snapshot from the future: Precision farming based on visualized data graphs
With modern tools like sensors and mobile devices, farmers can remotely and accurately monitor soil moisture, ambient temperature, and crop conditions in real-time. This makes it possible to flexibly adjust agronomic measures, like sowing, irrigation, fertilizer, and seed adjustment, based on diverse data sets, to better align crops with the soil available. Take maize, for example. Data-powered adaptive sowing can increase crop yield by 300 to 600 kilograms per hectare of land.
Visualized data graphs for agriculture can help farmers make informed decisions regarding soil fertility, water, and nutrient delivery across key crop growth stages. These graphs can also help farmers better understand information such as local topographical characteristics, climate conditions, and crop diseases or pests so that they can better estimate crop yields, implement agricultural measures, and adjust budgets accordingly.
Visualized data graphs can also be used to monitor and manage agricultural production in real time, helping farmers make proactive, quick, and precise responses to changes in their environment. For example, in the event of extreme weathers, farmers can use this data to rapidly locate affected areas, develop solutions, and mitigate negative impacts on their yields.
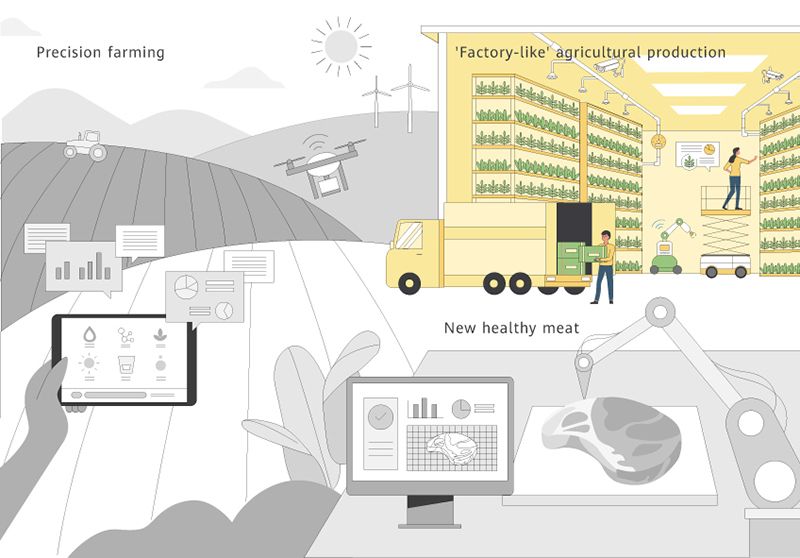
Taking a "factory-like" approach to protect agricultural production from environmental conditions
Snapshot from the future: A new form of agriculture in intelligent vertical farms
In vertical farms, every step of the cultivation process, from sowing, to fertilizing, to harvesting, is closely monitored, with farmers precisely controlling light, temperature, water, and nutrient delivery based on the needs of each crop. By controlling every stage of crop growth and adjusting environmental parameters as needed, farmers are able to artificially create the ideal environment for their plants.
Vertical farms have three main advantages:
- They don't need pesticides or soil, and reduce agricultural water waste.
- They are not affected by climate, providing consistent and ideal conditions for fresh produce.
- They provide smart agricultural models that are globally replicable.
Recent pilot programs for vertical farms have found that, if harvested every 16 days, a 7,000 square meters area can yield a staggering 900,000 kilograms of vegetables every year.
More Outlooks